Labeled diagram of Acer motherboard.
You may choose to click on the images to the right and explore what a motherboard looks like in more detail, but our primary emphasis is just what it does. Besides, motherboards do not all look alike. (Compare to image below.) It's a bit like lifting the hood on your car. You don't have to be a mechanic to know where to add windshield washer fluid. One of my goals is simply to take the mystery out of all that "stuff". It would be useful to open an old desktop PC just to actually see the parts. While I don't recommend this with a laptop or hand-held device, the concepts are pretty much the same. That goes for servers, mainframes and supercomputers, as well.We will talk about a few things you might do yourself to upgrade your computer in the last section of this module. Simply looking inside your computer can tell you if you have an open bay to add another hard disk and if you can add memory (or have to replace it).
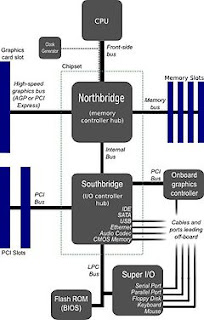
Logical layout of a motherboard
A motherboard is an electronic circuit board in a computer which interconnects hardware devices attached to it — which is to say, all of the system hardware. At a minimum it includes one or more Central Processing Units (CPU), and the main processing activity of the computer takes place on it. However, other connected printed circuit boards may contain their own pre-processing or post-processing CPUs, to take some of the load off of the motherboard; these, together with other plug-in boards without CPUs, may be called "daughter boards". It was called a "mother" board in relation to these. A PC motherboard generally has a series of slots, allowing daughter boards to be plugged in directly. Other connectors on the motherboard allow communication through cables with various peripheral devices, both inside and outside the
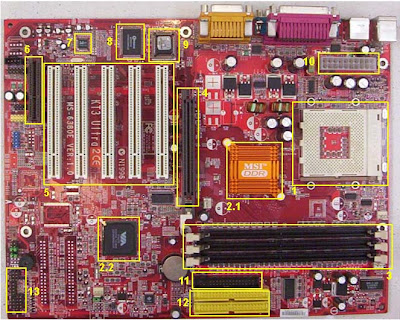
An ATX computer motherboard with labeled parts.
ATX motherboard legend1. Processor socket
2. Chipset
3. RAM slots
4. AGP graphic card slot
5. PCI slots
6. CNR modem slot
7. Audio chip
8. I/O chip
9. BIOS
10. ATX power connector
11. Floppy drive connector
12. ATA connectors
13. Connectors for buttons,
indicator lights etc.
The external ports (connections) are along the top edge (right hand side). A face-on view is shown below.
Ports
Ports are used by a motherboard to interface with electronics both inside and outside of the computer. Integrated ports are those that are part of, directly wired to, the motherboard. Internal integrated ports are used to connect devices inside the system unit. External ports may be connected to the motherboard directly (integrated) or by circuit boards that are inserted into slots on the motherboard. It is often possible to add new external ports by inserting such a circuit board into an open slot. The external integrated ports are generally grouped together as shown below. Expansion card ports are arranged in a row of equal sized rectangular slots (see graphics/video and network cards below).
Typical integrated motherboard ports (see top view above) — public domain image
| 1. & 2. PS/2 (mouse, keyboard) | 3. RJ-45 Ethernet | 4. USB | 5. Serial (terminal, modem) |
| 6. parallel (printer) | 7. VGA monitor | 8. DA-15 (old networking) | 9. audio |
PS/2
PS/2 connector
PS/2 ports were for connecting peripherals such as your mouse (1 above) and keyboard (2 above) to the computer, but are now outdated. PS/2 based mice and keyboards have now been replaced by USB ports as the popular standard. This trend for USB over PS/2 started in circa 2004.
Ethernet cable
RJ-45Wired Ethernet connection (3 above). Looks like a (bigger) telephone/modem jack. The cable itself is referred to by its category (e.g. CAT 5) and basic type, UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair).
USB
Different USB connectors. From left to right: male Micro USB B-Type, proprietary (not USB), male Mini USB (5-pin) B-type, female A-type, male A-type, male B-type. Shown with a centimeter ruler. Female A-type connector (4th from left) is "upside down" to show the pins.
USB (4 above), or Universal Serial Bus, is a connectivity specification, currently at version 3 (V3). They are very common today, connecting flash drives and many peripherals. Modern desktop systems have should have 4-8 on the back of the computer and at least two on the front.
USB is one of the most successful interconnect in computing history. V1 operates at 1.5 Mbps (low speed) or 12 Mbps (full speed), V2 (high speed) at 480 Mbps, and V3 (super speed) at up to 5Gbps. It can be found in over 2 billion PC and mobile devices. USB has strong consumer brand recognition and a reputation for ease-of-use.
USB connectors are sometimes used to supply power, generally to recharge hand-held devices like a smartphone.
USB connector types
Different USB connectors. From left to right: male Micro USB B-Type, proprietary (not USB), male Mini USB (5-pin) B-type, female A-type, male A-type, male B-type. Shown with a centimeter ruler. Female A-type connector (4th from left) is "upside down" to show the pins.
What is a Computer Bus?
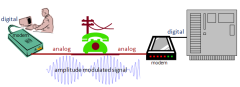
Computer bus analogy
A computer bus carries data from one device to another. It's more like an electricity bus than the vehicle. In terms of vehicles, the (computer) bus would be the road being traveled, with the vehicles on the road being the data. Serial busses allow one vehicle at a time, while parallel busses support multiple vehicles. Modern serial busses are faster because the data (vehicles) travel at a greater speed. Serial
Serial connector
An outdated piece of technology, serial ports (5 above) were most often used to connect the mouse and keyboard. By circa 2000, most personal computers stopped relying on serial ports and were replaced by PS/2 and/or USB ports.Parallel
Parallel printer cable
Parallel ports (6 above) are used to connect other peripherals such as joysticks, and more commonly, printers. Similar to the serial port, this technology is slowly being phased out in favor of USB. Parallel ports can still be found in many motherboards today.VGA
VGA cable for monitor
A VGA (7 above), or Video Graphics Array, connector is used to connect a monitor or other video equipment. The same connector is sometimes used for high definition television and is sometimes called an RGB connector.DA-15
The DA-15 port shown (8 above) has been used for network connectivity and for video output.
Audio
Audio ports
The audio input and stereo output ports (9 above) connect to external speakers, a microphone, head sets, and possibly a game. The external ports are color coded by industry standard.Firewire
Firewire PCI Expansion Card
Firewire cables: 4 & 6 circuit
Technically known as the IEEE 1394 interface, but dubbed by Apple as Firewire (not shown above), this connection medium hoped to surpass USB in terms of speed and popularity. While it did outperform USB v2 in speed tests, uptake was very limited due to the existing widespread use of USB.Firewire is the standard for high definition audio and video transfer and may be found on many digital camcorders.
Also known by the brand names i.LINK and Lynx.
eSATA [src]
eSata Cable
SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) is a computer bus interface for connecting to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives and optical drives inside the system box. eSATA is an external port for drives.Modem
For many years the telephone, or voice band, modem (not shown above) was the primary means of connecting desktop and laptop PCs to the Internet. Modems have not gone away, as broadband connections are not available in all areas.
A standard telephone modem uses your existing analog telephone line at speeds up 56 Kbps. The speed is limited by the quality of the phone line connection — extraneous noise lowers the actual throughput.
Broadband connections (to be discussed in the section on networks) also use modems of a different type. They are still called modems because their essential function is the same — they convert digital signals to analog and modulate them on an analog medium when sending information, and reverse this process when receiving it. Hence, they MOdulate and DEModulate.
Modem ports and connectors look a lot like Ethernet (RJ-45). A lot of networking was initially done with phone cables. Technically, they are called Category 3 UTP.
SCSI
SCSI connectors
Pronounced "scuzzy", SCSI (not shown above) was used primarily as a connection interface for tape drives and hard disk drives. SCSI has been superseded in favor of newer and cheaper technologies such as USB and Firewire in the home market.SCSI provides a high-speed (up to 5 Gbps) bus interface that allows up to 8 or 16 devices to be attached. It is still used for high-end workstations and servers.
Slots
On the typical desktop PC, a number of slots are provided on the motherboard (see image above) for attaching devices. One use of these slots is to expand or add to the ports available for external devices, as noted above. Graphics, audio and networking may be incorporated on the motherboard, but are often handled by (daughter) circuit boards added into slots. These are often pre-installed on your computer, but may be replaced (upgraded) as needed.
Adding devices to laptop computers, after purchase, is problematic. Simply opening and closing the case can be a challenge and is not recommended for the novice, although manufactures usually provide fairly easy access to the RAM memory and hard disk. To allow for expansion through external devices, laptops often have an external slot (or port).
ExpressCard
Comparison of Express Card and PC card
The ExpressCard and slot (not shown above) is used primarily on laptop computers. It replaces the older PC Card (also called PCMCIA) shown at right. The ExpressCard comes in two sizes, although the ExpressCard/34 may be used in an ExpressCard/54 slot.Hardware that may be plugged into a computer via an ExpressCard includes connect cards, FireWire 800 (1394B), USB 3.0, 1Gb/sec Ethernet, Serial ATA external stick drives, solid-state drives, external enclosures for desktop size PCI Express graphics cards, wireless network interface cards, TV tuner cards, common access card (CAC) readers, and sound cards.[src]
Other card slots may also be available, such a PC cards, smart cards, and secure digital cards
Graphics Card
Graphics Card Model: PNY, nVidia 6600GT
Graphics cards are also called video cards or a video adapter. They are in all PCs, but may be integrated on the motherboard. Graphic cards generate output images that can be displayed on the monitor. While many graphics cards are built into the motherboard these days, enthusiasts will invest in stand-alone graphics cards with more powerful processing capabilities. This allows for heavy image editing, or better rendering and frame rates in computer games.Graphics cards are designed to offload rendering from the CPU. Graphics cards are powered by the motherboard and require a PCI-X or PCIe slot to install. Some cards require more power and thus will need a 6-8 pin connector that runs directly to the power supply. Graphics cards also include on-board memory for efficient rendering. Typical sizes include 128-1024MB of memory. Today, high end graphics cards have multiple core processors that are largely parallel to increase texture fill and process more 3D objects in real time.
Sound Card
Creative Labs Soundblaster Live
A sound card, also referred to as an audio card, facilitates the input and output of audio signals to and from a computer under the control of computer programs. Sound cards for computers were uncommon until 1988, which left the single internal PC speaker as the only way early PC software could produce sound and music.Uses of a sound card include the audio component's for multimedia applications such as games, video/audio editing software and music composition. Most computers today have sound capabilities built into the motherboard, while others require additional expansion cards.
The external ports are color coded by industry standard.
Network Interface Card
Network card with both BNC "Thinnet" (left) and Ethernet RJ-45 (right)
A Network Interface Card (NIC), also called a network card, network adapter, or LAN Adapter is a piece of computer hardware designed to allow computers to communicate over a computer network. Used for remote communication via cable. Data is transmitted over a cable network. The NIC connects computers to the Internet and other devices, such as printers. Many modern motherboards have NICs built in by default.Most laptops also provide a wireless adapter or wireless network interface controller (WNIC). This device allows your laptop to communicate via a radio transceiver with a wireless (Wi-Fi) network. A WNIC can be added using a USB port or ExpressCard slot.
http://cs.sru.edu/~mullins/cpsc100book/module03_internalHardware/module03-01_internalHardware.html

.jpg)

















+and+Ethernet+RJ-45+(right).jpg)
0 comments:
Post a Comment